IEEE CVPR 2024
HHMR: Holistic Hand Mesh Recovery by Enhancing the Multimodal Controllability of Graph Diffusion Models
Mengcheng Li1, Hongwen Zhang2, Yuxiang Zhang1, Ruizhi Shao1, Tao Yu1, Yebin Liu1
1Tsinghua University, 2Beijing Normal University.
Abstract
Recent years have witnessed a trend of the deep integration of the generation and reconstruction paradigms. In this paper, we extend the ability of controllable generative models for a more comprehensive hand mesh recovery task: direct hand mesh generation, inpainting, reconstruction, and fitting in a single framework, which we name as Holistic Hand Mesh Recovery (HHMR). Our key observation is that different kinds of hand mesh recovery tasks can be achieved by a single generative model with strong multimodal controllability, and in such a framework, realizing different tasks only requires giving different signals as conditions. To achieve this goal, we propose an all-in-one diffusion framework based on graph convolution and attention mechanisms for holistic hand mesh recovery. In order to achieve strong control generation capability while ensuring the decoupling of multimodal control signals, we map different modalities to a shared feature space and apply cross-scale random masking in both modality and feature levels. In this way, the correlation between different modalities can be fully exploited during the learning of hand priors. Furthermore, we propose Condition-aligned Gradient Guidance to enhance the alignment of the generated model with the control signals, which significantly improves the accuracy of the hand mesh reconstruction and fitting. Experiments show that our novel framework can realize multiple hand mesh recovery tasks simultaneously and outperform the existing methods in different tasks, which provides more possibilities for subsequent downstream applications including gesture recognition, pose generation, mesh editing, and so on.
[arXiv (Coming Soon)] [Code (Coming Soon)]
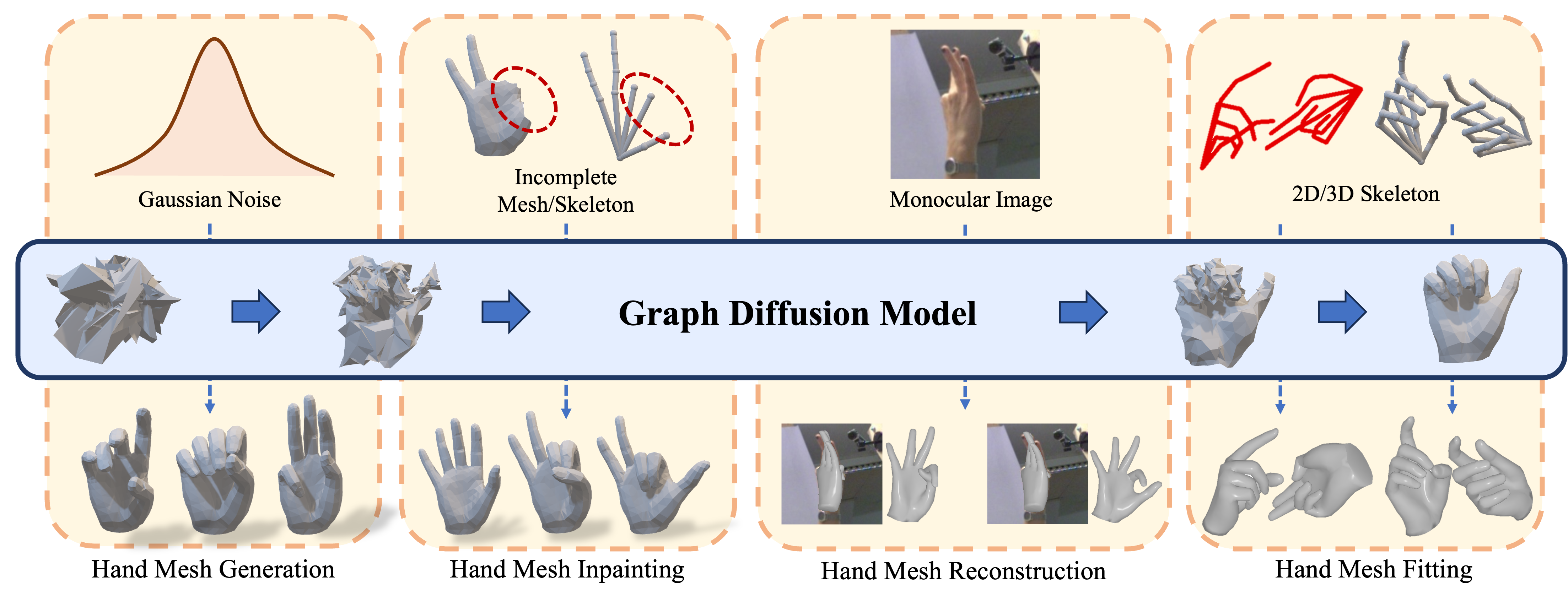
Fig 1. We introduce HHMR, a graph diffusion-based generation framework that are compatible with various human hand mesh recovery tasks.
Results
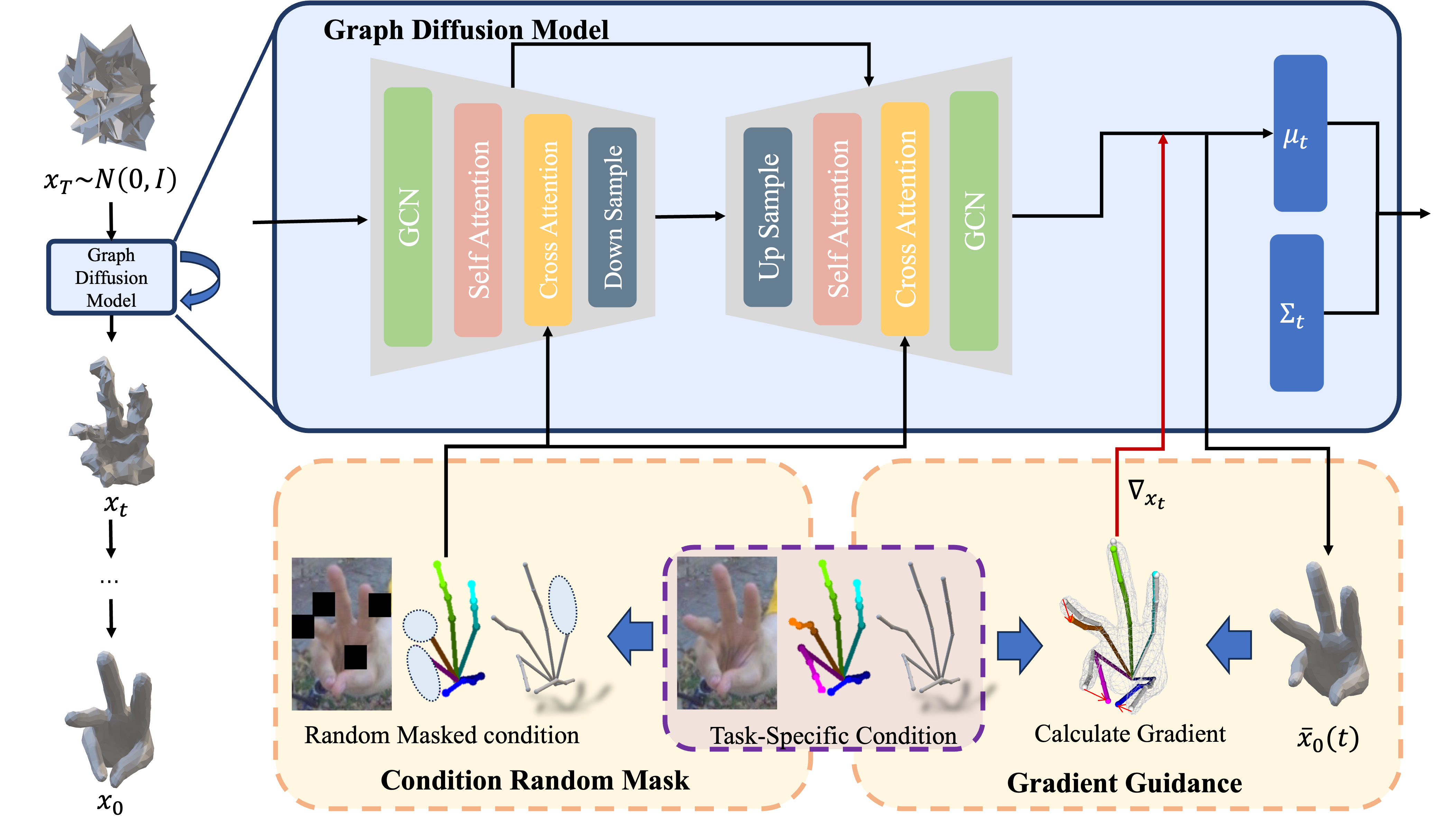
Fig 2. The pipeline of our graph diffusion model. With task-specific conditions, our model progressively removes noise from randomly Gaussian noise and directly reconstructs the complete hand meshes. Additionally, we introduce a gradient-based guidance to improve the alignment between the generated results and observations.
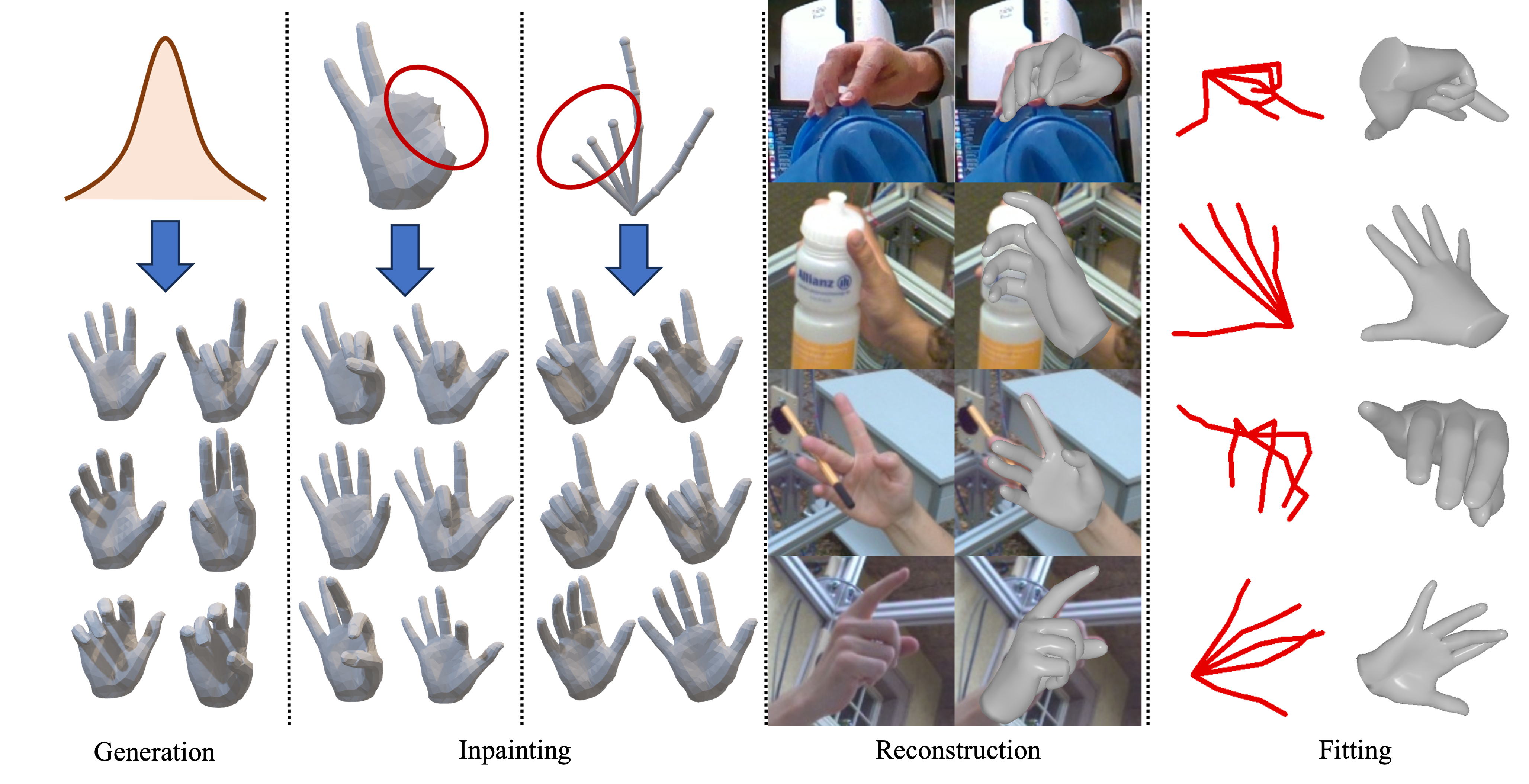
Fig 3. Qualitative results of our method for different downstream tasks. From left to right are i) hand mesh generation results from random Gaussian noise, ii) hand mesh inpainting from incomplete hand mesh or skeleton, iii) hand mesh reconstruction from monocular RGB image, and iv) hand mesh fitting from 2D skeletons.
Technical Paper
(Early access, not camera ready version)
Demo Video
Citation
Mengcheng Li, Hongwen Zhang, Yuxiang Zhang, Ruizhi Shao, Tao Yu, Yebin Liu. "HHMR: Holistic Hand Mesh Recovery by Enhancing the Multimodal Controllability of Graph Diffusion Models". In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024.
@inproceedings{Li2024HHMR,
title={HHMR: Holistic Hand Mesh Recovery by Enhancing the Multimodal Controllability of Graph Diffusion Models},
author={Mengcheng Li, Hongwen Zhang, Yuxiang Zhang, Ruizhi Shao, Tao Yu and Yebin Liu.},
booktitle={IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year={2024},
}
